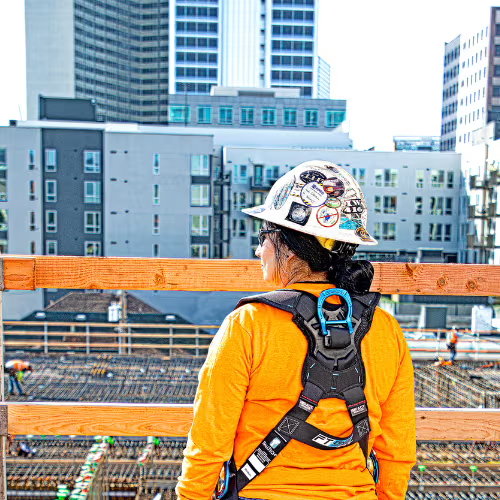
Fall Protection: Safeguarding Lives. Falls remain one of the leading causes of workplace injuries and fatalities across various industries. Whether working at heights, on scaffolding, or in confined spaces, employees face significant risks without adequate fall protection measures in place. In fact, according to the International Labour Organization (ILO), falls account for nearly 20% of all workplace accidents worldwide.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of fall protection, key prevention strategies, and the role that organizations must play in ensuring the safety of their workforce.
The Importance of Fall Protection
Fall protection isn’t just about adhering to regulations; it’s about creating a culture of safety and responsibility. For industries such as construction, manufacturing, and mining, fall hazards are inevitable. Workers on ladders, rooftops, or elevated platforms are especially vulnerable. However, proper fall protection can prevent serious injuries or fatalities, protect your business from costly fines, and boost overall productivity.
Compliance with national standards, such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulations in the U.S., is crucial. These standards require employers to implement fall protection measures when workers are at a height of six feet or more in general industries and four feet in construction settings.
Key Fall Protection Strategies
Effective fall protection includes a combination of hazard identification, training, and proper use of equipment. Below are five essential strategies to protect workers from falls:
1. Risk Assessment and Planning
Before any job begins, a thorough risk assessment must be conducted. Identifying potential fall hazards and planning how to mitigate them is the first step in fall protection. Areas that pose a high risk, such as unguarded edges or weak structural points, should be prioritized for protection.
2. Guardrails and Barriers
Guardrails are one of the most common and effective forms of passive fall protection. Installing guardrails, safety nets, and other barriers at elevated worksites provides a physical layer of defense that prevents workers from falling. These systems are crucial on scaffolds, walkways, and rooftops.
3. Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS)
When workers must operate at heights without the possibility of guardrails or barriers, Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS) are essential. PFAS includes a full-body harness, a lanyard, and an anchor point, all designed to stop a fall in progress and minimize injury. It’s vital that workers are trained in how to properly wear and adjust harnesses to ensure maximum protection.
4. Training and Education
No fall protection system is effective without proper training. Workers should receive regular training on identifying fall hazards, using fall protection equipment, and emergency procedures in the event of a fall. Employers should foster an environment where safety is taken seriously, and workers feel empowered to report hazards or unsafe conditions.
5. Routine Inspections and Maintenance
Fall protection equipment must be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure it remains in working order. Even the best equipment can fail if it’s worn, damaged, or improperly stored. Employers should implement a routine inspection schedule, and workers must be taught to inspect their gear before use.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Despite the availability of advanced fall protection systems, many companies still struggle with consistent implementation. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Cost Concerns: Investing in fall protection equipment and training can be costly upfront. However, the long-term savings from reduced injuries, insurance claims, and legal fees far outweigh the initial costs.
- Worker Compliance: Ensuring workers comply with safety regulations can be difficult, especially when they feel rushed to complete tasks. Building a strong safety culture and emphasizing the importance of safety gear is critical to overcoming this challenge.
- Limited Space: In some cases, fall protection systems like guardrails or nets aren’t feasible due to limited space. In such instances, personal fall arrest systems and temporary anchor points become essential. Fall Protection: Safeguarding Lives
Conclusion: Fall Protection Saves Lives
Ensuring the safety of workers at heights is not optional—it’s a critical part of any organization’s safety program. Fall protection, when properly implemented, can reduce injuries and save lives. Employers must prioritize hazard identification, invest in reliable equipment, and foster a culture of safety through training and regular inspections.
By staying proactive and compliant with fall protection regulations, businesses can protect their employees, minimize risks, and maintain productivity in even the most hazardous work environments.
For more in-depth safety strategies and resources, stay connected with OHS Magazine, your trusted source for workplace safety insights and solutions.